Margin-based Loss 설명
24 Oct 2021 | Machine Learning목차
이 글에서는 Margin-based Loss를 정리한다.
Margin-based Loss
간단하게는 true target $y$와 prediction result $\hat{y}$의 곱 $y\hat{y}$을 갖고 계산하는 loss라고 생각할 수 있다.
Distance-based Loss와는 다르게, true target과 prediction 사이의 차이(difference)에 대해 신경 쓰지 않는다. 대신, target의 sign과 얼마나 잘 agree(혹은 일치)하는지에 기반한 prediction을 penalize한다.
Margin-based Loss는 단 하나의 변수 $v = yf(x)$에 의해 정의될 수 있고, 적절히 선택된 함수 $\phi : \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$에 대해 $V(f(\vec{x}), y) = \phi(yf(\vec{x})) = \phi(v)$이다.
보통 이진 분류(binary classification)에서 유용하게 사용된다.
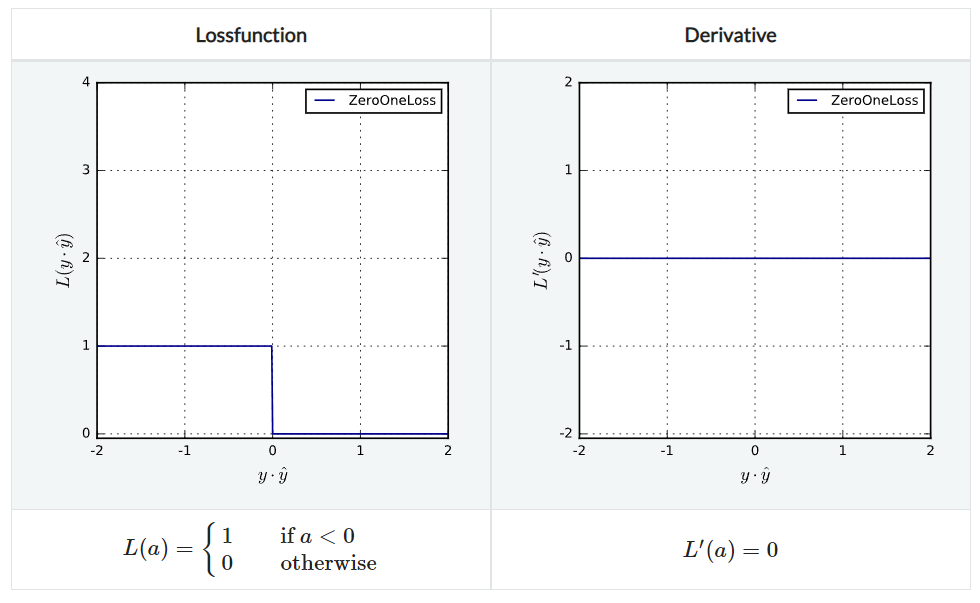
ZeroOneLoss
전통적인 분류 loss로, 간단히 말해서 맞으면 loss가 0, 틀리면 1이다. non-convex, non-continuous하며 그냥은 잘 쓰이지 않는다. 대신 surrogate loss인 L1HingeLoss 등을 쓴다.
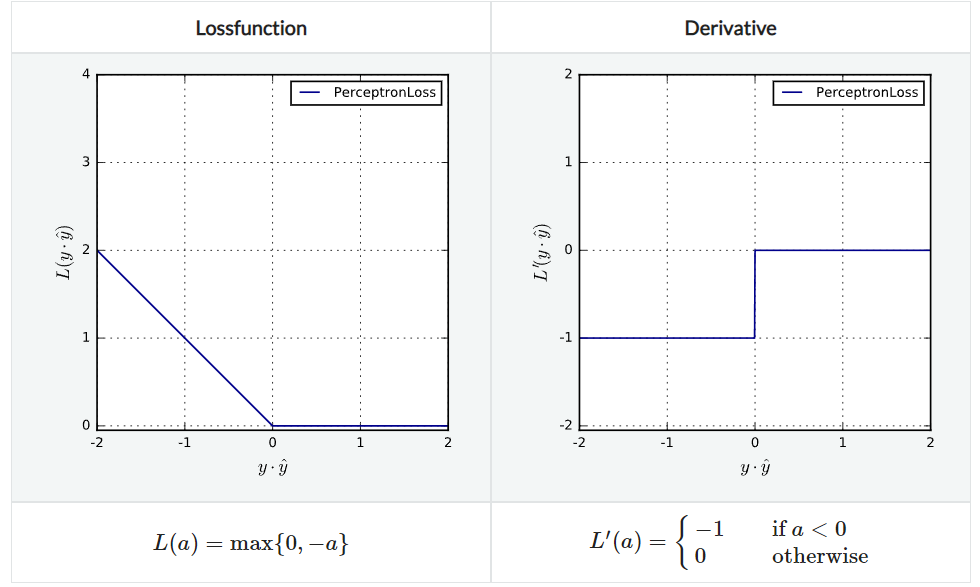
PerceptronLoss
agreement $\le 0$일 수록 penalize하는 방법으로 Lipschitz continuous, Lipschitz convex하지만 strict convex하지는 않다.
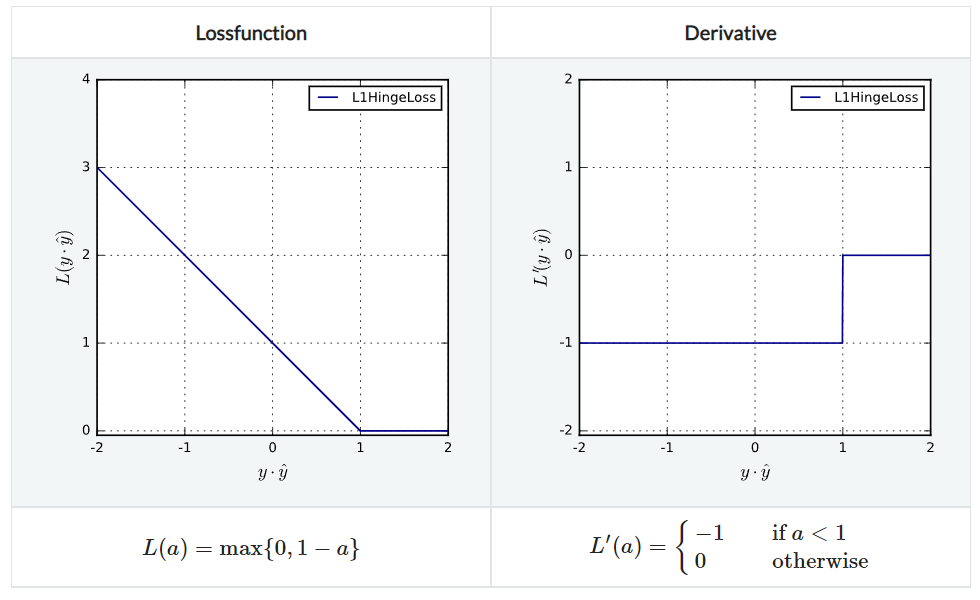
L1HingeLoss
PerceptronLoss와 비슷하지만 agreement $\le 1$인 경우에 penalize한다는 점이 다르다.
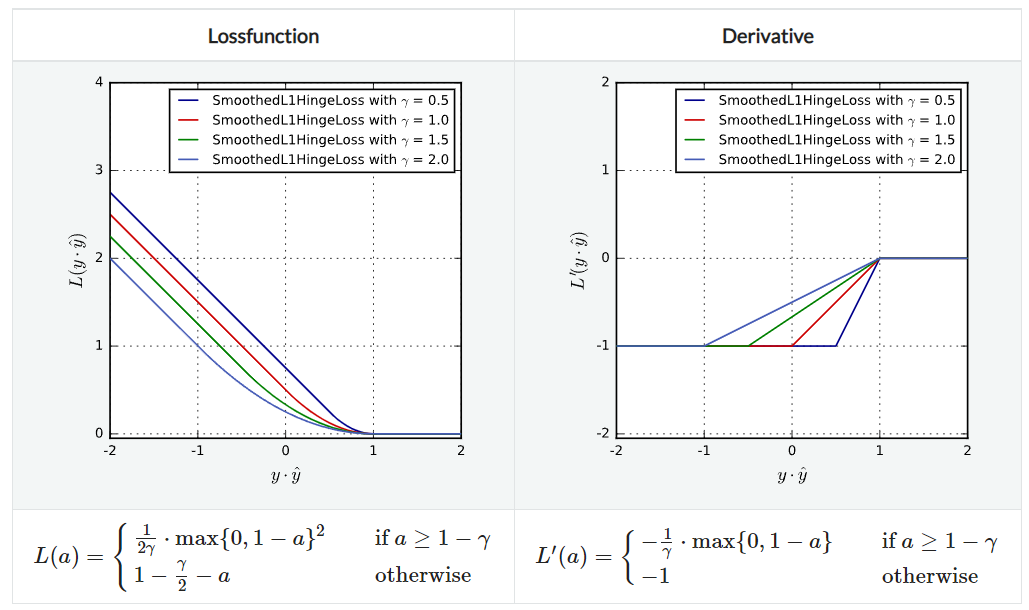
SmoothedL1HingeLoss
L1 Hinge Loss와 비슷하지만, $y\hat{y}=1$인 지점에서 미분이 안 되는 점을 보완한 것으로 부드럽게 꺾이는 것을 볼 수 있다. 여전히 strict convex하지는 않다. parameter로 $\gamma$와 $\alpha$가 있다.
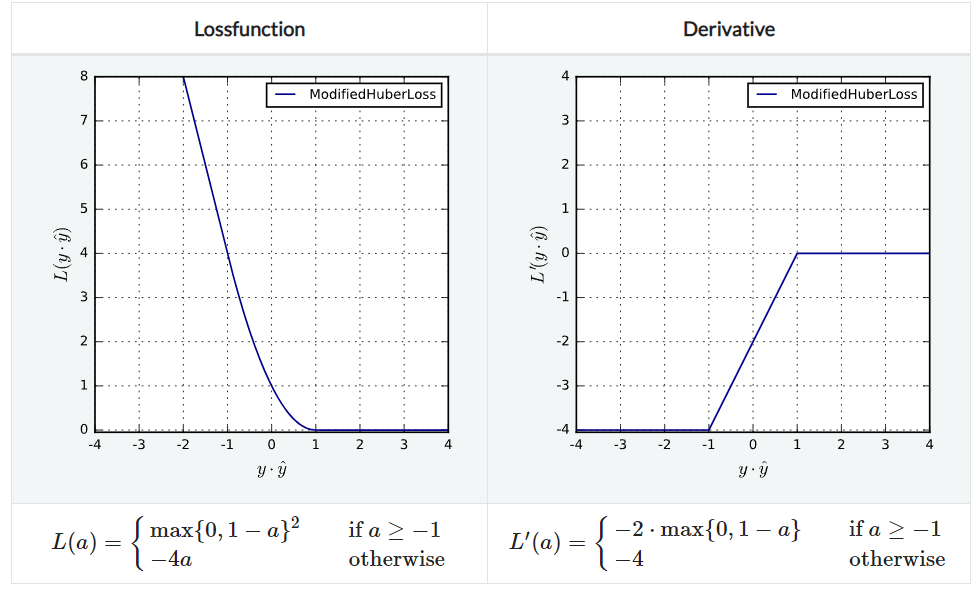
ModifiedHuberLoss
SmoothedL1HingeLoss에서 $\gamma=2$인 특수한 경우이다.
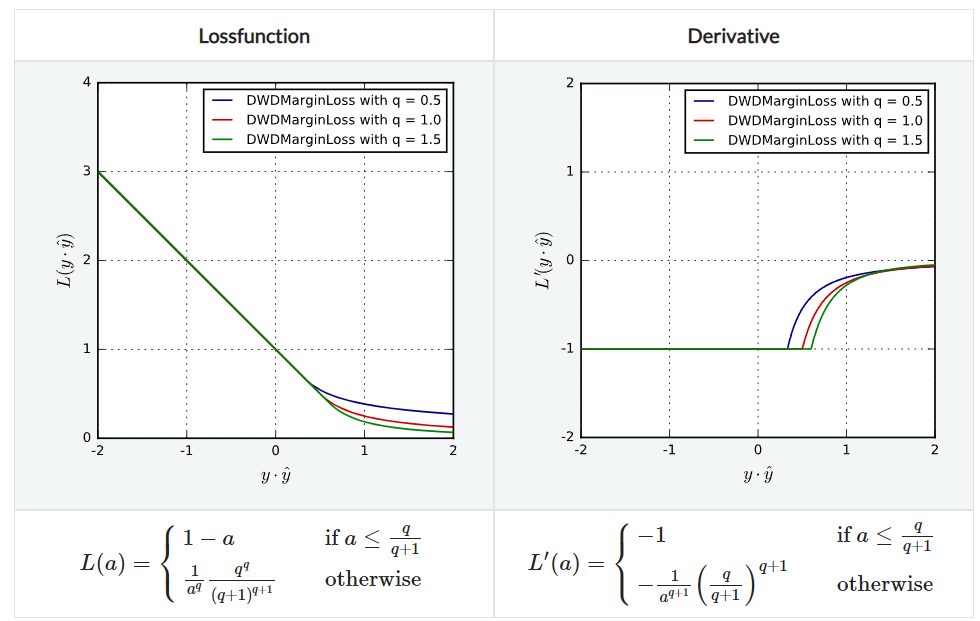
DWDMarginLoss
Distance Weighted Discrimination margin loss이다. L1HingeLoss의 미분가능한 일반적인 버전으로 SmoothedL1HingeLoss와는 다른 loss 함수이다.
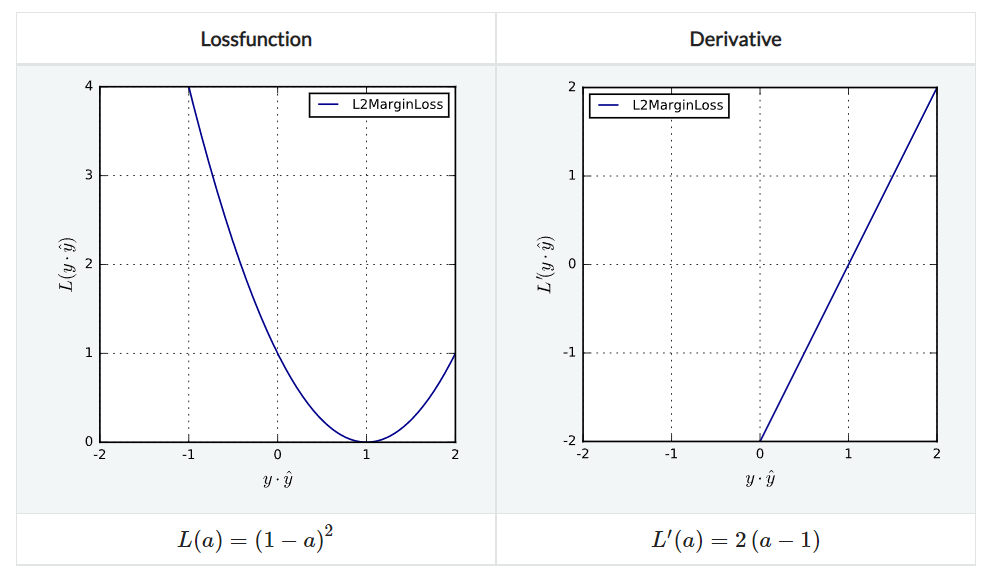
L2MarginLoss
L2 loss를 생각하면 된다. agreement $\ne 1$인 경우에 모두 이차함수적으로 penalize하는 방식이다. Lipschitz continuous하며 strongly convex하다.
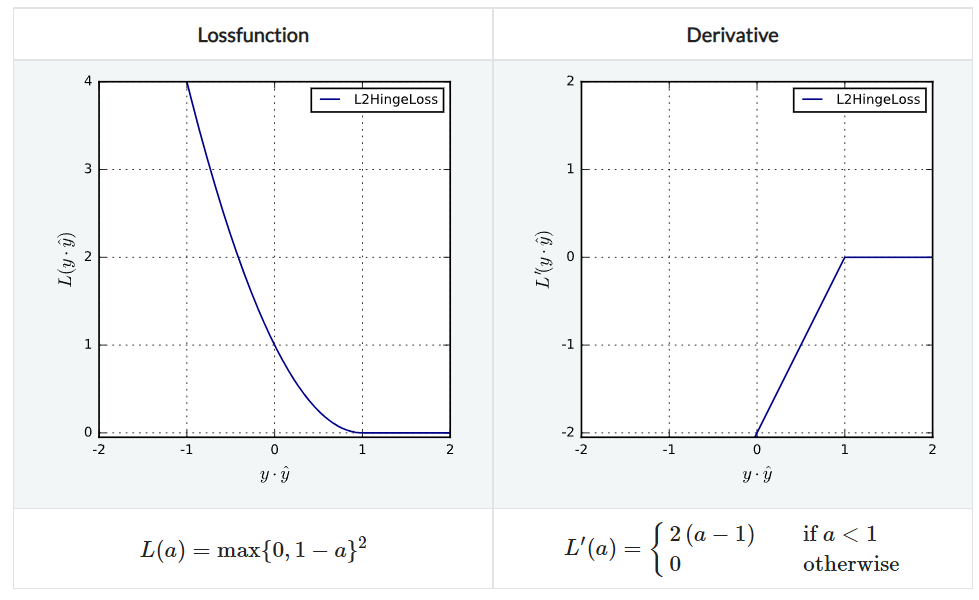
L2HingeLoss
L1HingeLoss와 L2 margin loss를 합친 것이라고 생각하면 된다. agreement $\lt 1$인 경우에 이차함수적으로 penalize한다. 지역적으로 Lipschitz continuous하며 convex하지만 strongly convex하지는 않다.
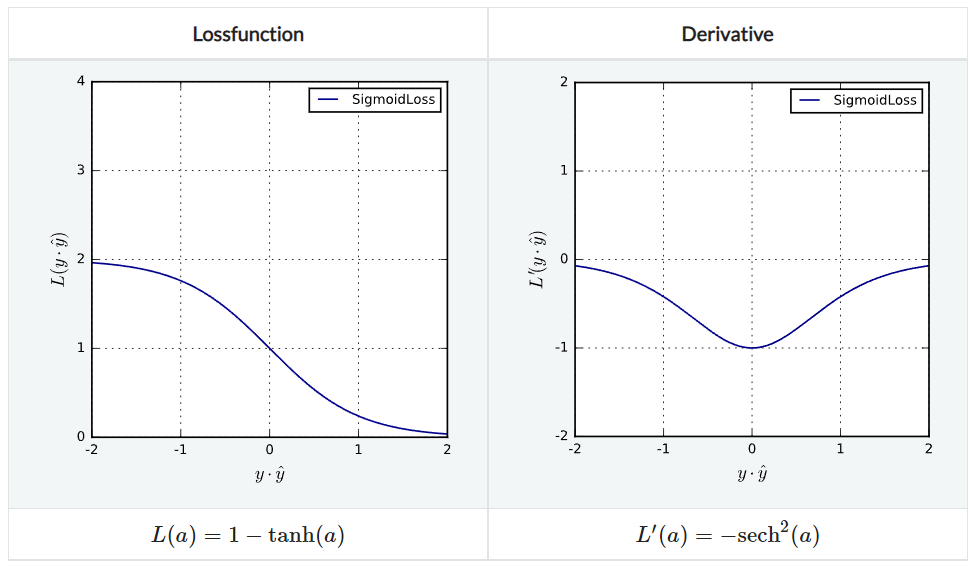
SigmoidLoss
$(0, 2)$ 범위에서 모든 예측 결과에 대해 penalize하는 방법으로 무한히 미분 가능하며 Lipschitz continuous하지만 non-convex하다.
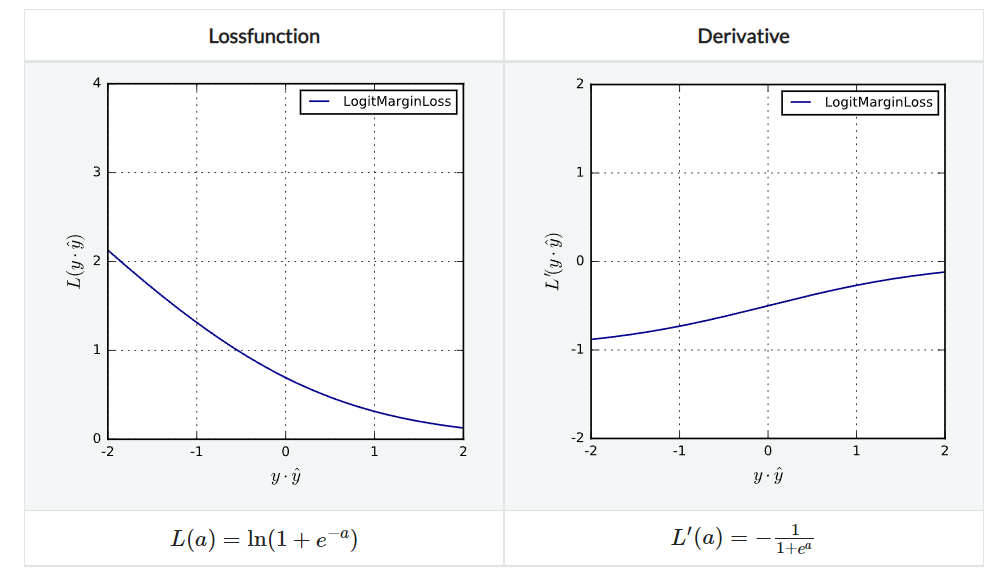
LogitMarginLoss
Logistic loss의 margin 버전이다. 무한히 미분 가능하며 Lipschitz continuous하다.
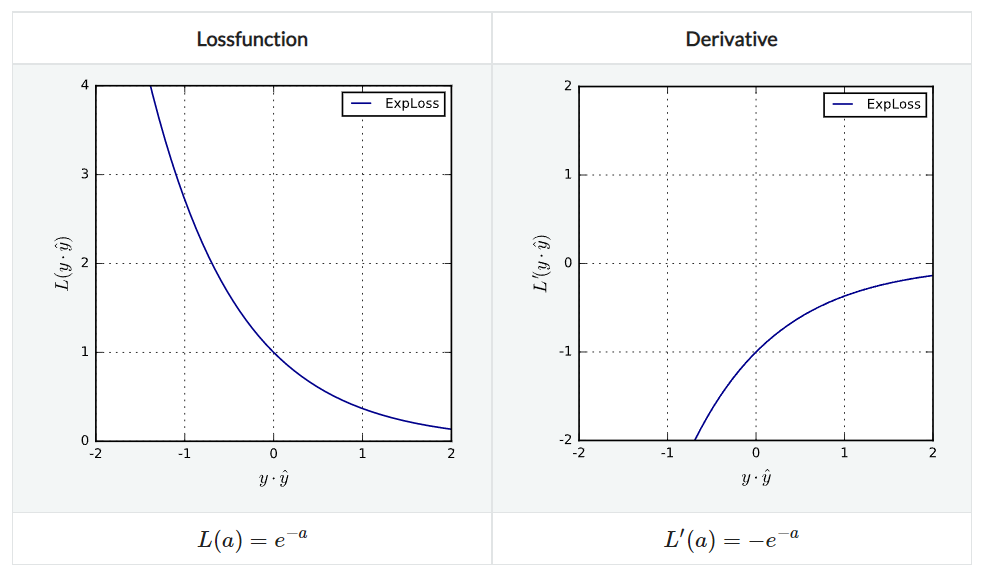
ExpLoss
모든 예측 결과를 지수적으로 penalize한다. 무한히 미분 가능하며 Lipschitz continuous하고 또한 strictly convex하지만, clipable하지는 않다.