matplotlib 사용법(python matplotlib.pyplot 사용법)
12 May 2023 | matplotlib seaborn usage목차
이 글에서는 python matplotlib의 사용법을 정리한다.
따로 명시하지 않으면 이 글에서의 예제 데이터는 다음으로 설정한다.
data = pd.DataFrame(data={
'A': [1,4,3,6,5,8,7,9],
'B': [6,5,7,8,9,9,8,9],
'C': [8.8,7.7,6.6,5.5,4.4,3.3,2.2,1.1]
})
matplotlib 설치
설치는 꽤 간단하다.
pip install matplotlib
import는 관례적으로 다음과 같이 한다.
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
Font 설정
아무 설정을 하지 않으면 한글이 깨지는 경우가 많다.
RuntimeWarning: Glyph 44256 missing from current font.
font.set_text(s, 0.0, flags=flags)
보통 다음과 같이 설정해주면 된다.
from matplotlib import rcParams
rcParams["font.family"] = "Malgun Gothic"
rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False
참고로 설정 가능한 폰트 목록을 확인하고 싶다면 다음 코드를 실행해 보자.
import matplotlib.font_manager
fpaths = matplotlib.font_manager.findSystemFonts()
font_names = []
for i in fpaths:
f = matplotlib.font_manager.get_font(i)
font_names.append(f.family_name)
print(font_names[:5])
for fn in font_names:
if 'malgun' in fn.lower():
print(fn)
Jupyter 전용 기능
다음 magic command를 사용사면 plt.show() 함수를 사용하지 않아도 그래프를 보여준다.
%matplotlib inline
plt.scatter(x=[1,2,3], y=[4,5,6])
보통의 환경이라면 plt.show() 함수를 사용해야 그래프가 보인다. PyCharm이라면 SciView 창에서 열린다.
그래프 종류
산점도(scatter)
plt.scatter(x=[1,2,3], y=[4,5,6])

선 그래프(plot)
plt.plot(data.index, data['B'])
# 하나만 입력하면 기본 index로 그려진다.
plt.plot(data['C'])
# 한 번의 plot() 호출로 여러 개를 그릴 수 있다. 순서는 x, y, fmt 순으로 입력할 수 있다.
t = np.arange(0., 5., 0.2)
plt.plot(t, t, 'r--', t, t**2, 'bs-', t, t**3, 'g^-.')
plot()은 list나 DataFrame뿐 아니라 dictionary도 그래프로 나타낼 수 있다.
data_dict = {'x': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 'y': [2, 3, 5, 7, 11]}
plt.plot('x', 'y', data=data_dict)
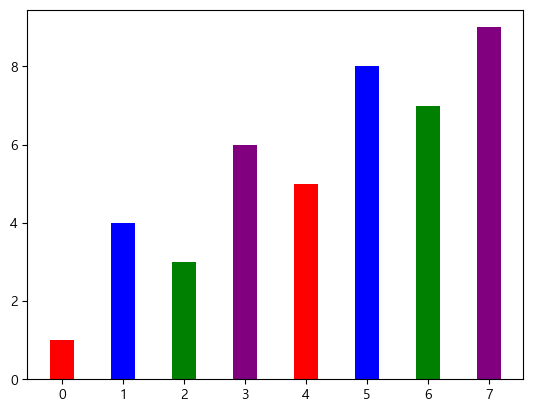
막대 그래프(bar)
plt.bar(data.index, data['B'])
2개 그룹 동시 표시
stack해서 사용하는 방법은 다음과 같이 bottom 옵션을 사용한다.
p1 = plt.bar(data.index, data['B'], color='red', alpha=0.7)
p2 = plt.bar(data.index, data['C'], color='blue', alpha=0.7, bottom=data['B'])
# plot이 여러 개인 경우 plt.legend()는 그냥 넣으면 legend가 출력되지 않는다.
나란히 놓는 방법은 bar의 width 옵션과 x좌표를 조정하면 된다.
p1 = plt.bar(data.index-0.2, data['B'], color='red', alpha=0.7, width=0.4)
p2 = plt.bar(data.index+0.2, data['C'], color='blue', alpha=0.7, width=0.4)
plt.legend((p1, p2), ('B', 'C'), fontsize=12)
boxplot
x = np.random.normal(50, 5, 100)
plt.boxplot(x)
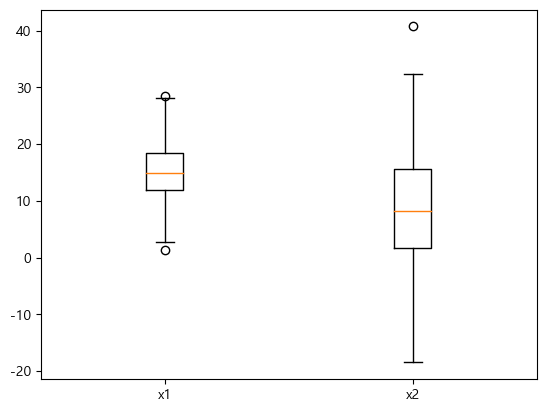
여러 boxplot을 한 번에 그리려면 리스트에 담아서 전달한다.
x1 = np.random.normal(15, 5, 500)
x2 = np.random.normal(10, 10, 100)
plt.boxplot([x1, x2])
plt.xticks([1, 2], ["x1", "x2"])
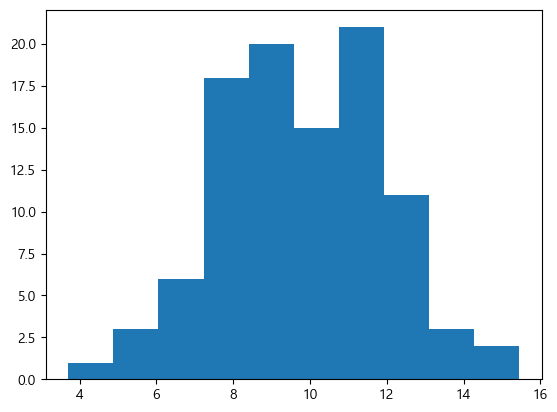
Histogram
구간 개수는 bins으로 설정한다.
x = np.random.normal(10, 2, 100)
plt.hist(x, bins=10)
Heatmap
matshow라는 함수가 있지만 이건 seaborn의 heatmap이 더 편하다.
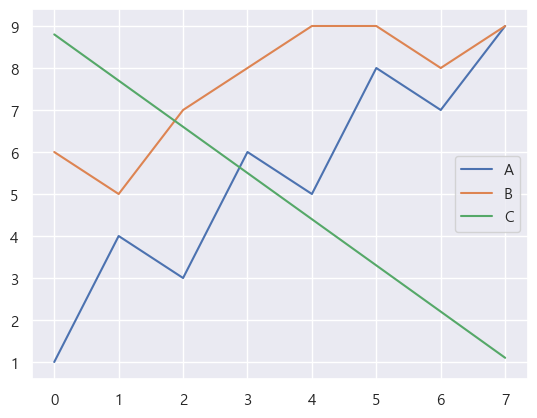
pd.DataFrame.plot
- pandas의 dataframe에서
.plot()method를 호출하면 바로 그래프를 그릴 수 있다.- 종류는
line, bar, barh, hist, box, scatter등이 있다.barh는 수평 막대 그래프를 의미한다.
- 종류는
data.plot(kind='line')
좀 더 자세하게 설정할 수도 있다. 이 글에 있는 스타일 설정을 대부분 적용할 수 있다.
data.plot(kind = "bar", y = ["B", "C"], figsize = (10, 6),
yticks=[0, 5, 10])
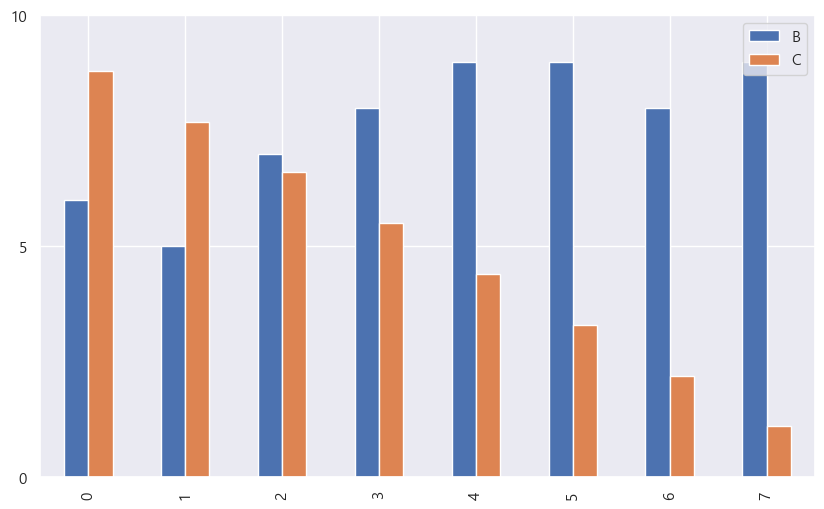
단 boxplot과 histogram은 y만 설정할 수 있다.
스타일 설정
더 많은 설정은 여기를 참고하자.
dashes옵션으로 직접 dash line을 조작할 수 있다.markevery옵션으로 마커를 만들 샘플을 추출할 수 있다. 옵션값이 5(int)면 5개의 샘플마다, float이면 상대적 거리에 따라 추출한다.visible옵션으로 선을 안 보이게 할 수 있다.fillstyle옵션으로 마커를 채우는 방식을 설정할 수 있다.full, left, right, bottom, top, none가능
format string(fmt)
색상, 마커, 선 스타일을 쉽게 지정할 수 있다.
plt.plot(data['A'], 'b.-', label='A')
plt.plot(data['B'], 'cv--', label='B')
plt.plot(data['C'], 'm|:', label='C')
plt.legend()
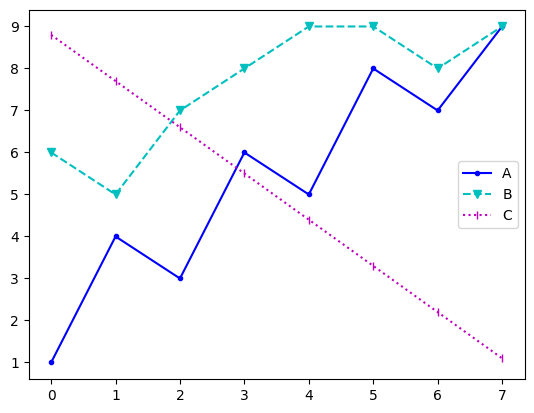
색상(color)
plt.plot(data['B'], label='B', color='red')
plt.plot(data['C'], label='C', color='green')
plt.legend()
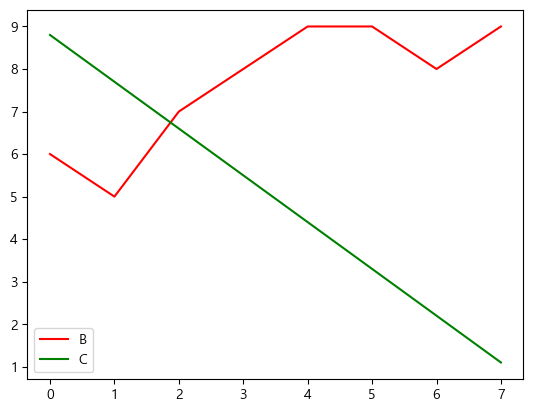
| fmt | color |
|---|---|
b |
blue |
g |
green |
r |
red |
c |
cyan |
m |
magenta |
y |
yellow |
k |
black |
w |
white |
선 스타일(linestyle), 두께(linewidth)
- 선 스타일은
linestyleparameter를 전달하며 기본값인solid와dashed, dotted, dashdot이 있다. - 선 두께는
linewidth로 설정하고 기본값은 1.5이다.
plt.plot(data['A'], label='A', linestyle='dashed', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(data['B'], label='B', linestyle='dotted', linewidth=3)
plt.plot(data['C'], label='C', linestyle='dashdot', linewidth=4)
plt.legend()
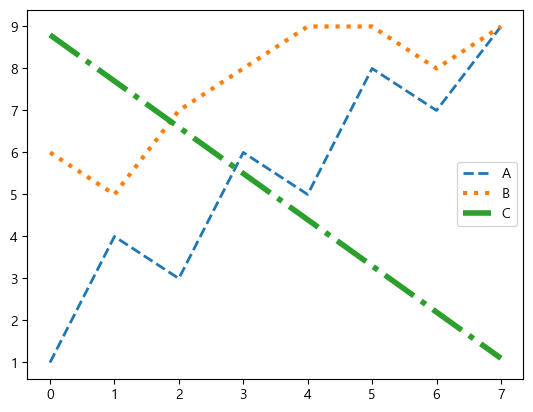
| fmt | linestyle |
|---|---|
- |
solid |
-- |
dashed |
: |
dotted |
-. |
dashdot |
수치로 직접 지정할 수 있다. 참고로 (0, (1, 1))은 dotted, (0, (5, 5))는 dashed, (0, (3, 5, 1, 5))는 dashdot과 같다.
plt.plot(data['A'], label='A', linestyle=(0, (1,1)), linewidth=2)
plt.plot(data['B'], label='B', linestyle=(0, (4,1)), linewidth=3)
plt.plot(data['C'], label='C', linestyle=(0, (1,4)), linewidth=4)
plt.legend()
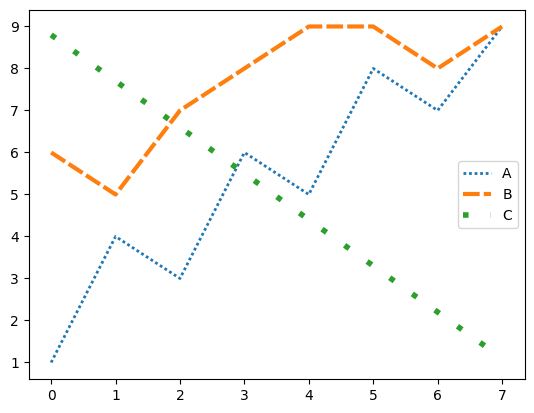
bar 스타일(width, color, linewidth)
bar의 두께를 설정할 수 있다. 각 데이터마다 다른 값을 주면 각각 다르게 설정할 수도 있다.
plt.bar(data.index, data['A'], width=0.4, color=["red", "blue", "green", "purple", "red", "blue", "green", "purple"], linewidth=2.5)
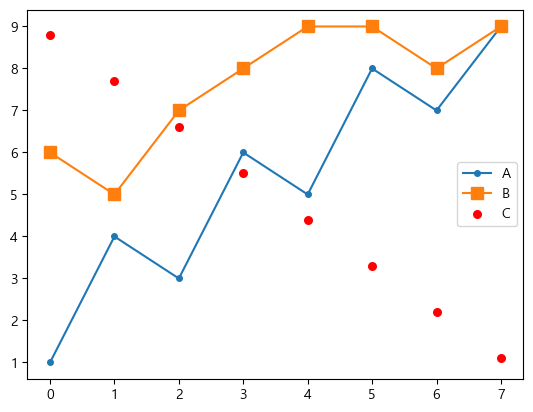
마커(marker)
각 data point마다 marker를 표시할 수 있다.
- 점:
., 원:o, 사각형:s, 별:*, 다이아몬드:D,d - marker의 사이즈도
markersizeparameter로 지정할 수 있다. - 산점도(scatter)의 마커 크기는
sparameter로 설정한다. 단 크기가 10배 차이난다.
plt.plot(data['A'], label='A', marker='o', markersize=4)
plt.plot(data['B'], label='B', marker='s', markersize=8)
plt.scatter(data.index, data['C'], label='C', marker='.', s=120, color='red')
plt.legend()
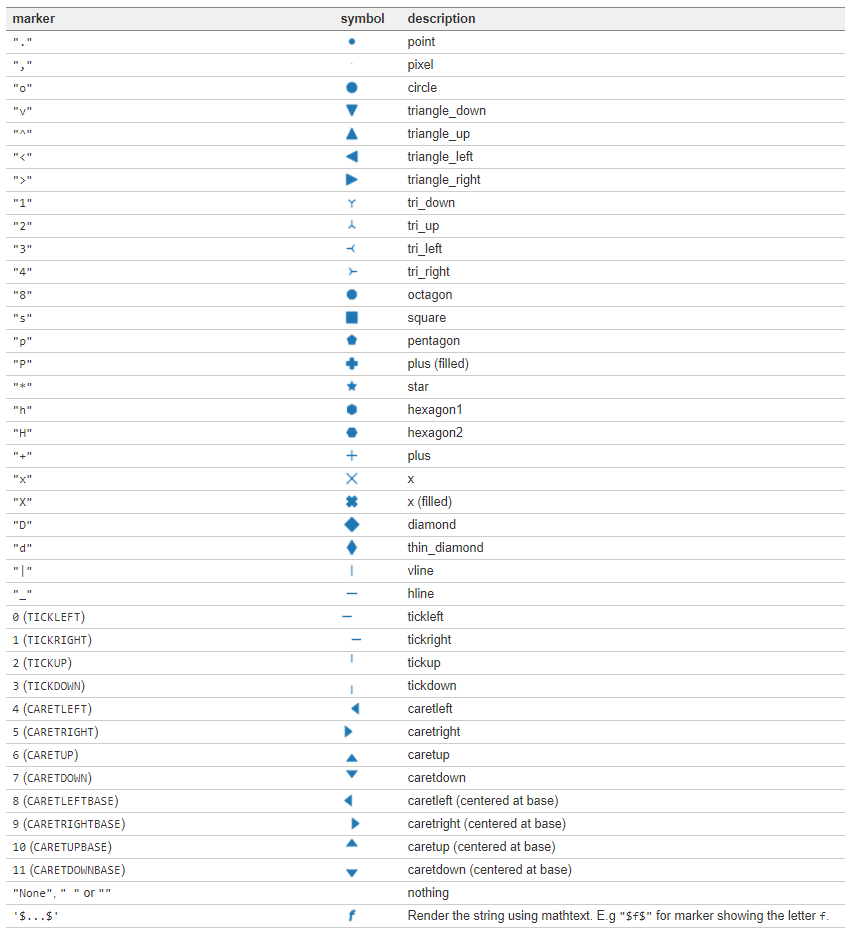
| fmt | marker | 설명 | fmt | marker | 설명 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
. |
point | 점 | s |
square | 사각형 |
, |
pixel | 픽셀 | p |
pentagon | 오각형 |
o |
circle | 원 | * |
star | 별 |
v |
triangle_down | 역삼각형 | h |
hexagon1 | 육각형 1 |
^ |
triangle_up | 삼각형 | H |
hexagon2 | 육각형 2 |
< |
triangle_left | 삼각형(왼쪽) | + |
plus | + 모양 |
> |
triangle_right | 삼각형(오른쪽) | x |
x | x 모양 |
1 |
tri_down | 삼각뿔(아래쪽) | D |
diamond | 다이아몬드 |
2 |
tri_up | 삼각뿔(위쪽) | d |
thin diamond | 얇은 다이아몬드 |
3 |
tri_left | 삼각뿔(왼쪽) | | |
vline | v line |
4 |
tri_right | 삼각뿔(위쪽) | _ |
hline | h line |
더 많은 마커 옵션이 있다.
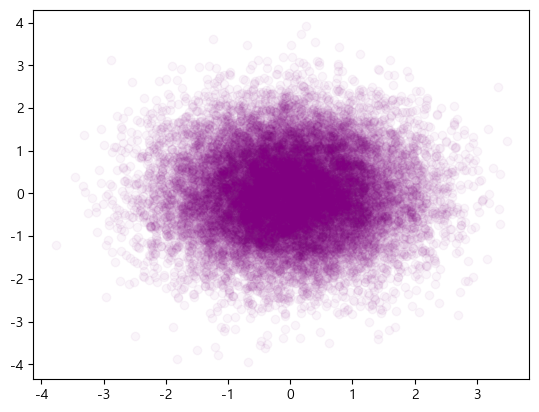
투명도(alpha)
데이터가 너무 많은 경우 투명도를 조절하면 좀 더 잘 보이게 할 수 있다.
import numpy as np
x = np.random.normal(0, 1, 16384)
y = np.random.normal(0, 1, 16384)
plt.scatter(x, y, alpha = 0.04, color='purple')
그래프 전체 설정
그래프 크기 설정
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 3))
plt.scatter(x=data.index, y=data['A'])
그래프 제목(title)
plt.scatter(x=data.index, y=data['A'])
plt.title("Gorio")
범례 설정(legend)
기본적으로 plot(label=...) 등으로 label을 등록하면, plt.legend()로 등록된 label들을 표시해주는 개념이다.
plt.scatter(x=data.index, y=data['A'], label='Gorio')
plt.legend()
legend 위치는 그래프를 가리지 않는 위치에 임의로 생성된다. 위치를 지정하려면 loc parameter를 설정한다.
plt.scatter(x=data.index, y=data['A'], label='Gorio')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
가능한 옵션을 총 9개이다. left, center, right, upper left, upper center, upper right, lower left, lower center, lower right
참고로 loc=(0.5, 0.5)와 같이 직접 수치를 지정할 수도 있다. loc=(0.0, 0.0)은 왼쪽 아래, loc=(1.0, 1.0)은 오른쪽 위이다.
legend() 메서드에서도 label을 직접 등록하여 표시할 수 있다.
p1 = plt.bar(data.index-0.2, data['A'], color='red', alpha=0.7, width=0.4)
p2 = plt.bar(data.index+0.2, data['C'], color='blue', alpha=0.7, width=0.4)
plt.legend((p1, p2), ('A', 'C'), fontsize=12)
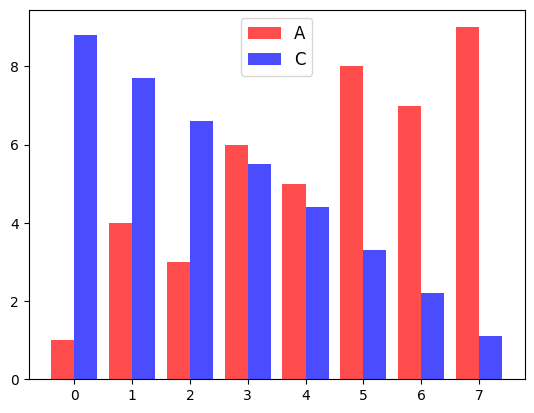
ncol 옵션으로 범례에 표시되는 텍스트의 열 개수를 지정할 수 있다.
p1 = plt.bar(data.index-0.2, data['A'], color='red', alpha=0.7, width=0.4, label='A')
p2 = plt.bar(data.index+0.2, data['C'], color='blue', alpha=0.7, width=0.4, label='C')
plt.legend(ncol=2)
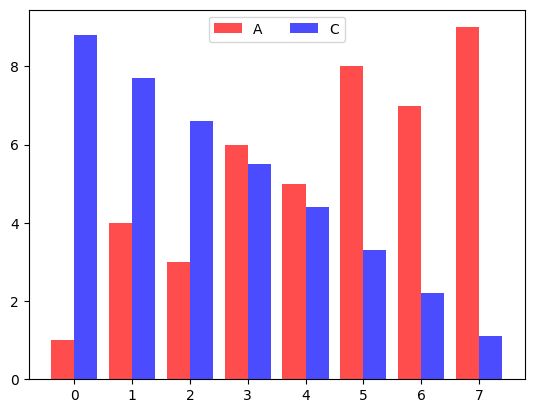
각종 다양한 스타일을 지정할 수 있다.
p1 = plt.bar(data.index-0.2, data['A'], color='red', alpha=0.7, width=0.4, label='A')
p2 = plt.bar(data.index+0.2, data['C'], color='blue', alpha=0.7, width=0.4, label='C')
plt.legend(frameon=True, shadow=True, facecolor='inherit', edgecolor='green', borderpad=0.8, labelspacing=1.1)
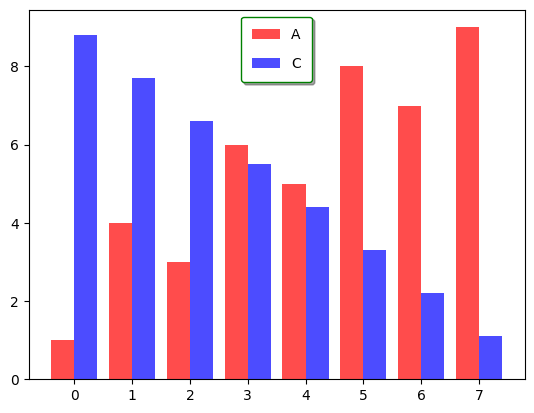
더 자세한 설정은 여기에서 확인 가능하다.
x, y축 설정
축 제목(xlabel, ylabel)
plt.scatter(x=data.index, y=data['A'])
plt.xlabel("x axis")
plt.ylabel("y axis")
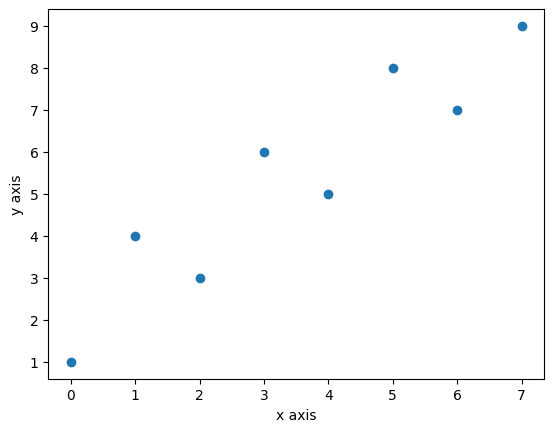
축 제목과 축 간 거리는 labelpad로 조정한다.
plt.plot(data.index, data['A'])
plt.xlabel("x axis", labelpad=20)
plt.ylabel("y axis", labelpad=-1)
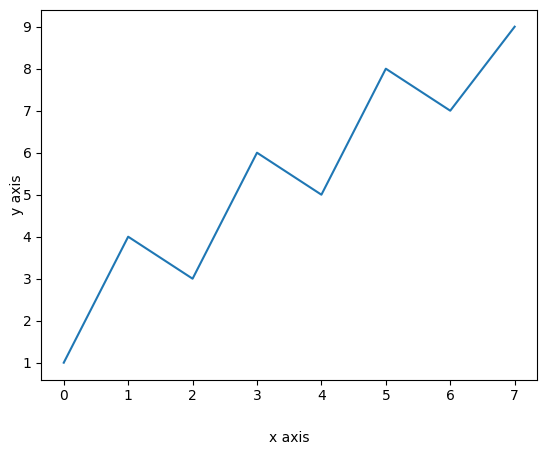
폰트 설정도 할 수 있다.
font1 = {'family': 'serif',
'color': 'b',
'weight': 'bold',
'size': 14
}
font2 = {'family': 'fantasy',
'color': 'deeppink',
'weight': 'normal',
'size': 'xx-large'
}
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [2, 3, 5, 7])
plt.xlabel('x Axis', labelpad=15, fontdict=font1)
plt.ylabel('y Axis', labelpad=20, fontdict=font2)
축 범위 설정(xlim, ylim, axis)
각 함수를 호출하면 return value로 x축, y축, x 및 y축의 최솟값/최댓값을 얻을 수 있다.
plt.scatter(x=data.index, y=data['A'])
xmin, xmax = plt.xlim(left=0, right=10)
ymin, ymax = plt.ylim(bottom=0, top=10)
# 아래 한 줄로도 쓸 수 있다.
# xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax = plt.axis([0,10,0,10])
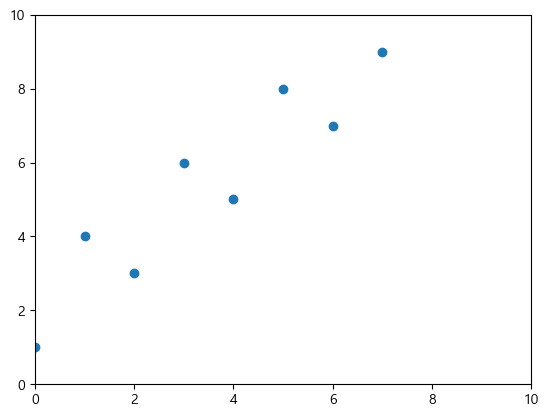
참고로 left, right, bottom, top 중 설정하지 않은 값은 데이터 최솟값/최댓값에 맞춰 자동으로 설정된다.
범위를 수치로 직접 설정하는 대신 그래프의 비율이나 scale을 조정할 수 있다.
scaled의 경우 다음과 같이 x축 간격과 y축 간격의 scale이 같아진다.
plt.scatter(x=data.index, y=data['A'])
xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax = plt.axis('scaled')
# (-0.35000000000000003, 8.450000000000001, 0.6, 9.4)
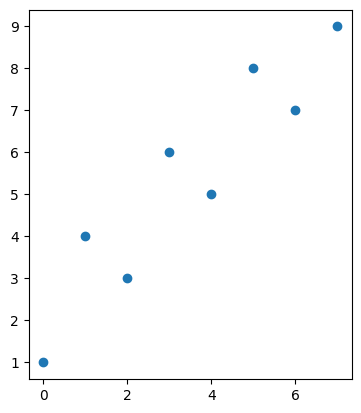
다음과 같은 옵션들이 있다: 'on' | 'off' | 'equal' | 'scaled' | 'tight' | 'auto' | 'normal' | 'image' | 'square'
눈금 값 설정(xticks, yticks)
ticks에 tick의 위치를 지정하고, labels에 원하는 tick 이름을 지정할 수 있다.
plt.scatter(x=data.index, y=data['A'])
plt.xticks(ticks=[0,3,6], labels=['zero', 'three', 'six'])
plt.ylim(bottom=0, top=10)
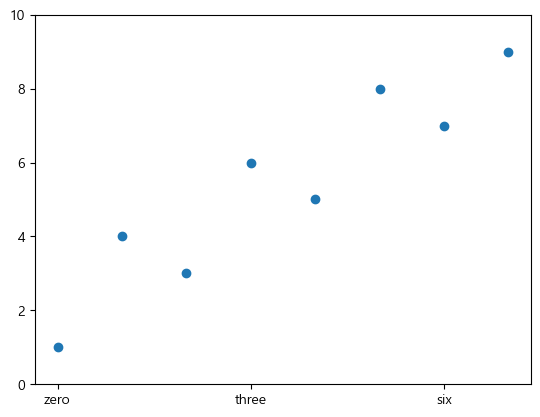
xticks나 yticks에 값을 1개만 주면 ticks parameter가 설정된다.
plt.scatter(x=data.index, y=data['A'])
plt.xticks([0,3,6])
plt.ylim(bottom=0, top=10)
참고로 막대그래프는 기본적으로 막대의 중심 좌표를 기준으로 계산하지만 align parameter를 주면 왼쪽 위치로 계산할 수 있다.
plt.bar(data.index, data['B'], align='edge')
plt.xticks([0,3,6], ['zero', 'three', 'six'])
그래프 저장(savefig)
plt.scatter(x=data.index, y=data['A'])
plt.savefig("gorio.png", dpi=300)
dpi는 dot per inch의 약자이다. 높을수록 해상도가 좋아지고 파일 크기도 커진다.
References
- https://wikidocs.net/book/5011
- https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.lines.Line2D.html

